In this tutorial, we will deploy docker containers on Amazon ECS using AWS Fargate. We will be using ECS-CLI to build the stack step by step. Amazon ECS Command Line Interface (CLI) is a command line tool for Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) that provides high-level commands to simplify creating, updating, and monitoring clusters and tasks from a local development environment. In the future, I will build the same stack using CloudFormation.
There are two parts to this tutorial
- We will build and run a simple Python web application with Docker Compose. The application uses the Flask framework and maintains a hit counter in Redis. This tutorial is available on the Docker website here so I will not cover the details.
- Then we will deploy the image to ECS using ECS-CLI and FARGATE
Services Used:
- AWS CLI
- ECS CLI
- Amazon CloudWatch
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
- AWS Fargate
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Docker
- Flask
- Redis
Prerequisites
- IAM Identity Center user with appropriate permissions
- AWS CLI is installed – see my previous post here
- Docker Desktop is installed
- ECS-CLI (not to be confused with AWS CLI) is installed and configured – follow the directions here
Steps
- Build your image using Dockerfile, run it locally and validate that it executes successfully (I am using the sample application from Docker for this tutorial)
- Rebuild the image with changes to app.py and deploy the image to ECR
- Create a cluster and security group
- Create ecs-params.yml and docker-compose.yml files and configure the cluster
- Compose a service
- Validate your implementation
- Clean up resources
STEP 1 : Docker Compose
I have very small variation from the Docker tutorial, but listing all the files below with the changes highlighted. My folder name is testapp and that’s why you will notice the default naming convention of the containers and images with testapp.
app.py
import time
import redis
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
cache = redis.Redis(host='redis', port=6379)
# change to localhost for deploying to ECS
#cache = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379)
def get_hit_count():
retries = 5
while True:
try:
return cache.incr('hits')
except redis.exceptions.ConnectionError as exc:
if retries == 0:
raise exc
retries -= 1
time.sleep(0.5)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
count = get_hit_count()
return 'Hello Maghilda! I have been seen {} times.\n'.format(count)Dockerfile
FROM python:3.11-alpine
WORKDIR /code
ENV FLASK_APP=app.py
ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST=0.0.0.0
RUN apk add --no-cache gcc musl-dev linux-headers
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
#install dependencies from list
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
EXPOSE 5000
COPY . .
CMD ["flask", "run"]compose.yml
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
networks:
- demoapp
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"
networks:
- demoapp
volumes:
- redisdata:/data
networks:
demoapp:
volumes:
redisdata:Build and run your app with compose
docker compose up -dWhen the docker compose finishes successfully, you can either go http://127.0.0.1:5000 or use a curl command to validate.
curl '127.0.0.1:5000'
Hello Maghilda! I have been seen 1 times.To check the env variable that you had defined in the Dockerfile
docker compose run web env
PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
HOSTNAME=b0d84f2608d6
TERM=xterm
LANG=C.UTF-8
GPG_KEY=A035C8C19219BA821ECEA86B64E628F8D684696D
PYTHON_VERSION=3.11.7
PYTHON_PIP_VERSION=23.2.1
PYTHON_SETUPTOOLS_VERSION=65.5.1
PYTHON_GET_PIP_URL=https://github.com/pypa/get-pip/raw/4cfa4081d27285bda1220a62a5ebf5b4bd749cdb/public/get-pip.py
PYTHON_GET_PIP_SHA256=9cc01665956d22b3bf057ae8287b035827bfd895da235bcea200ab3b811790b6
FLASK_APP=app.py
FLASK_RUN_HOST=0.0.0.0
HOME=/rootdocker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c05b5b095fab redis:alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes 6379/tcp testapp-redis-1
9e07c31729a6 testapp-web "flask run" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp testapp-web-1Login to the container
docker exec -it 9e07c31729a6 /bin/shYou will get the container terminal, run some commands in the container terminal. I ran the ls command which listed all the files. Once done, type exit.
/code # ls
Dockerfile app.py requirements.txt
__pycache__ compose.yaml Shut down the container and delete the image
docker compose down -vSTEP 2: Rebuild the image with changes to app.py and deploy the image to ECR
For the image to work in ECS, update the app.py. Change the redis connection from redis to localhost as follows:
#cache = redis.Redis(host='redis', port=6379)
# change to localhost for deploying to ECS
cache = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379)Then build the image again but without docker compose
docker build -t testapp .Tag the new image
docker tag testapp 123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dockerimages:mnewtagCreate a repository in ECR. I named it dockerimages
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name dockerimages --region us-east-1
{
"repository": {
"repositoryArn": "arn:aws:ecr:us-east-1:123456789012:repository/dockerimages",
"registryId": "123456789012",
"repositoryName": "dockerimages",
"repositoryUri": "123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dockerimages",
"createdAt": "2024-01-16T13:53:20-05:00",
"imageTagMutability": "MUTABLE",
"imageScanningConfiguration": {
"scanOnPush": false
},
"encryptionConfiguration": {
"encryptionType": "AES256"
}
}
}Login to ECR from Docker
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin 123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
Login SucceededPush the newly created image from Docker to ECR
docker push 123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dockerimages:mnewtag
The push refers to repository [123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dockerimages]
5ad795cc690c: Pushed
a10eca000a2f: Pushed
mnewtag: digest: sha256:02ec90be72edeb611f1222f548e5884ad8dfce204f693575cf5d9e0bf5d71296 size: 2412aws ecr list-images --repository-name dockerimages
{
"imageIds": [
{
"imageDigest": "sha256:02ec90be72edeb611f1222f548e5884ad8dfce204f693575cf5d9e0bf5d71296",
"imageTag": "mnewtag"
}
]
}STEP 3: Create a cluster and a security group
This will launch a cloudformation stack
ecs-cli up --cluster maghilda-cluster --launch-type FARGATE
INFO[0000] Created cluster cluster=maghilda-cluster region=us-east-1
INFO[0001] Waiting for your cluster resources to be created...
INFO[0001] Cloudformation stack status stackStatus=CREATE_IN_PROGRESS
VPC created: vpc-02b89083fd596fab1
Subnet created: subnet-0ad8279daf5983c83
Subnet created: subnet-03060b21523ea37b5
Cluster creation succeeded.aws ecs describe-clusters \
--include ATTACHMENTS \
--clusters maghilda-cluster
{
"clusters": [
{
"clusterArn": "arn:aws:ecs:us-east-1:123456789012:cluster/maghilda-cluster",
"clusterName": "maghilda-cluster",
"status": "ACTIVE",
"registeredContainerInstancesCount": 0,
"runningTasksCount": 0,
"pendingTasksCount": 0,
"activeServicesCount": 0,
"statistics": [],
"tags": [],
"settings": [],
"capacityProviders": [],
"defaultCapacityProviderStrategy": [],
"attachments": []
}
],
"failures": []
}Create a security group
aws ec2 create-security-group --group-name "maghilda-fargate-service-discovery-sg" \
--description "Maghilda Fargate Service Discovery security group" \
--vpc-id "vpc-02b89083fd596fab1"
{
"GroupId": "sg-0ee81ee6e7c955957"
}Create ingress rules to allow 5000 traffic
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id "sg-0ee81ee6e7c955957" --protocol \
tcp --port 5000 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
{
"Return": true,
"SecurityGroupRules": [
{
"SecurityGroupRuleId": "sgr-0fdd8b43e8f6c61f3",
"GroupId": "sg-0ee81ee6e7c955957",
"GroupOwnerId": "123456789012",
"IsEgress": false,
"IpProtocol": "tcp",
"FromPort": 5000,
"ToPort": 5000,
"CidrIpv4": "0.0.0.0/0"
}
]
}STEP 4: Create ecs-params.yml and docker-compose.yml files and configure the cluster
ecs-params.yml
version: 1
task_definition:
task_execution_role: ecsTaskExecutionRole
ecs_network_mode: awsvpc
task_size:
mem_limit: 0.5GB
cpu_limit: 256
run_params:
network_configuration:
awsvpc_configuration:
subnets:
- "subnet-0ad8279daf5983c83"
- "subnet-03060b21523ea37b5"
security_groups:
- "sg-0ee81ee6e7c955957"
assign_public_ip: ENABLEDdocker-compose.yml. This is not the same as compose.yml file above
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: "123456789012.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dockerimages:mnewtag"
ports:
- "5000:5000"
logging:
driver: awslogs
options:
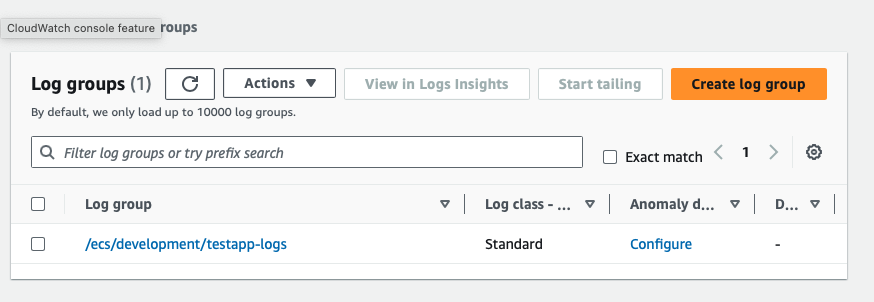
awslogs-group: /ecs/development/testapp-logs
awslogs-region: us-east-1
awslogs-stream-prefix: maghilda
redis:
image: "public.ecr.aws/docker/library/redis:6.2-bookworm"Configure the cluster with FARGATE as the launch type
ecs-cli configure --cluster maghilda-cluster --region us-east-1 --default-launch-type FARGATE --config-name ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config
INFO[0000] Saved ECS CLI cluster configuration ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config. This is saved in the ecs config file
cat ~/.ecs/config
version: v1
default: ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config
clusters:
ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config:
cluster: maghilda-cluster
region: us-east-1
default_launch_type: FARGATESTEP 5: Compose a service
This is where the magic happens.
ecs-cli compose --project-name maghilda-testapp \
service up --cluster-config ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config \
--cluster maghilda-cluster --create-log-groups
INFO[0000] Using ECS task definition TaskDefinition="maghilda-testapp:1"
INFO[0000] Auto-enabling ECS Managed Tags
INFO[0011] (service maghilda-testapp) has started 1 tasks: (task 61653f47e8de41dfa86927f79dd0c557). timestamp="2024-01-16 15:52:37 +0000 UTC"
INFO[0067] (service maghilda-testapp) has started 1 tasks: (task 87cb0a1384f348ec82da68ccc6ff3bc5). timestamp="2024-01-16 15:53:35 +0000 UTC"
INFO[0305] Created an ECS service service=maghilda-testapp taskDefinition=“maghilda-testapp:1"
INFO[0036] Service status desiredCount=1 runningCount=1 serviceName=maghilda-testapp
INFO[0036] ECS Service has reached a stable state desiredCount=1 runningCount=1 serviceName=maghilda-testapp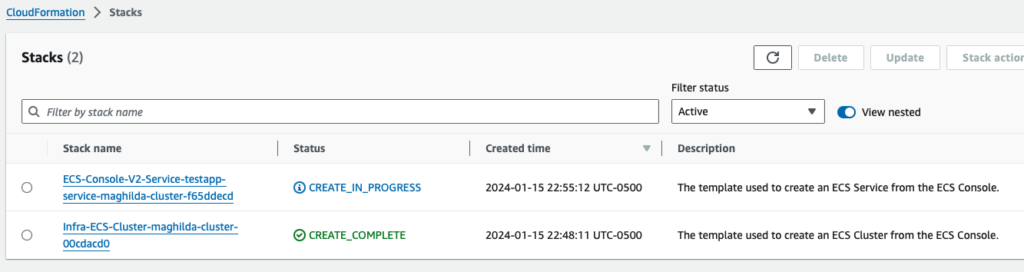
STEP 6: Validate your implementation
ecs-cli ps --cluster maghilda-cluster
Name State Ports TaskDefinition Health
maghilda-cluster/4be0c3641cb74194b1588510800f6577/redis RUNNING maghilda-testapp:1 UNKNOWN
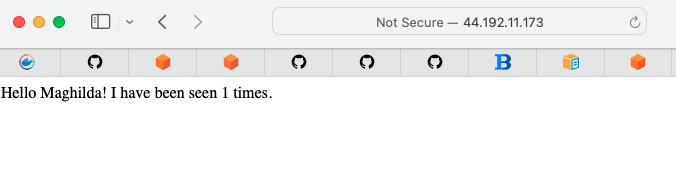
maghilda-cluster/4be0c3641cb74194b1588510800f6577/web RUNNING 44.192.11.173:5000->5000/tcp maghilda-testapp:1 UNKNOWNLoad the above url
Review the CloudWatch Logs via aws cli or the AWS management console
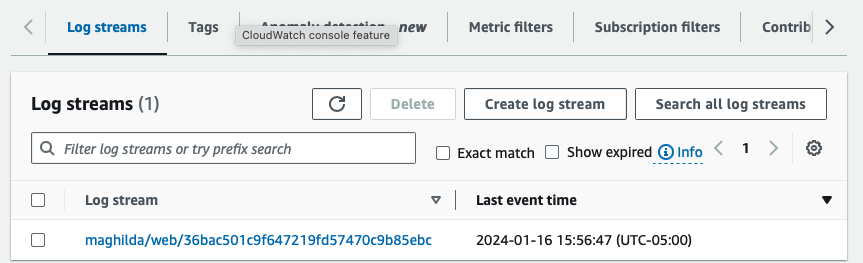
STEP 7: Cleanup resources
Delete the service
ecs-cli compose --project-name maghilda-testapp \
service down --cluster-config ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config \
--cluster maghilda-cluster
INFO[0000] Deleted ECS service service=maghilda-testapp
INFO[0000] Service status desiredCount=0 runningCount=1 serviceName=maghilda-testapp
INFO[0005] Service status desiredCount=0 runningCount=0 serviceName=maghilda-testapp
INFO[0005] ECS Service has reached a stable state desiredCount=0 runningCount=0 serviceName=maghilda-testappDelete the cluster. This can take a long time as CloudFormation tears down the stack.
ecs-cli down --force --cluster-config ecs-fargate-svs-discovery-config \
--cluster maghilda-cluster
####### this errored out as the cloudformation could not delete the vpc as it had dependencies. i had to delete the vpc manually
INFO[0000] Waiting for your cluster resources to be deleted...
INFO[0000] Cloudformation stack status stackStatus=DELETE_IN_PROGRESS
INFO[0031] Deleted cluster cluster=maghilda-clusterDelete the namespace
aws servicediscovery list-namespaces
{
"Namespaces": [
{
"Id": "ns-fd2a72lp4cvtuvnf",
"Arn": "arn:aws:servicediscovery:us-east-1:123456789012:namespace/ns-fd2a72lp4cvtuvnf",
"Name": "maghilda-cluster",
"Type": "HTTP",
"Properties": {
"DnsProperties": {
"SOA": {}
},
"HttpProperties": {
"HttpName": "maghilda-cluster"
}
},
"CreateDate": "2024-01-15T22:48:55.143000-05:00"
}
]
}
aws servicediscovery delete-namespace --id="ns-fd2a72lp4cvtuvnf"
{
"OperationId": "ncfzqtijxhicuygj4ziuw53ggekmoqvt-6pl90bxl"
}
aws servicediscovery list-namespaces
{
"Namespaces": []
}Delete ECR repository
aws ecr delete-repository --repository-name dockerimages --region us-east-1 --forceDelete CloudWatch Logs
aws logs delete-log-group --log-group-name /ecs/development/testapp-logsThis is the end of the tutorial. Hope you got something out of it.
References:
- https://docs.docker.com/compose/gettingstarted/
- https://github.com/docker/awesome-compose
- https://github.com/aws/amazon-ecs-cli
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/ProgrammingGuide.html
- https://github.com/aws-containers/demo-app-for-docker-compose
- https://gallery.ecr.aws/
- https://www.bogotobogo.com/DevOps/Docker/Docker-ECS-Service-Dicsovery-Redis-Flask.php
- https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/containers/automated-software-delivery-using-docker-compose-and-amazon-ecs/
- https://github.com/docker/compose-cli/blob/main/docs/ecs-compose-examples.md
- https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/containers/deploy-applications-on-amazon-ecs-using-docker-compose/
- https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/hands-on/deploy-docker-containers/
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/userguide/create-container-image.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/using_awslogs.html
- https://awscli.amazonaws.com/v2/documentation/api/latest/reference/ecs/index.html
